7 Reasons You Should Ditch (Cow) Milk
Cow milk is produced by female cows to nourish their young calves. During pregnancy, hormonal changes prepare the cow’s mammary glands for milk production. After calving, the cow begins producing colostrum, followed by regular milk. On dairy farms, cows are typically milked using mechanical milking machines, and the milk undergoes pasteurization and homogenization before packaging. While cow milk is a natural source of nutrition for calves, individuals may opt for alternative milk options due to lactose intolerance, dairy allergies, or personal preferences.
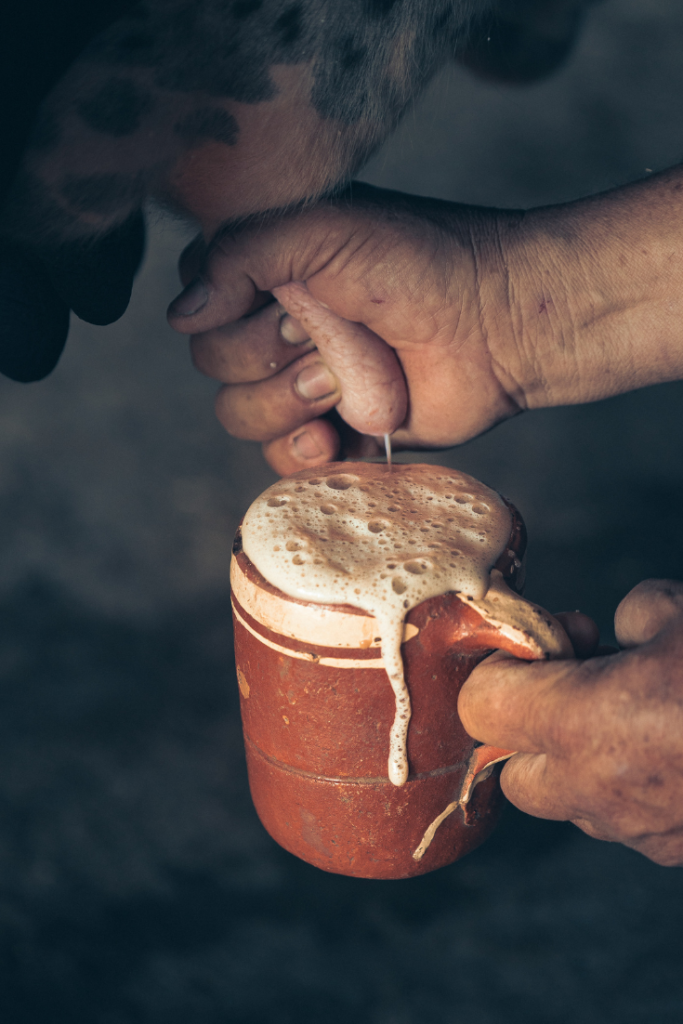


My family has always had a sensitivity to cow’s milk. I saw nothing wrong with it until I weaned myself from it after an oncologist recommended it and saw how I performed better in my sports. I quit regular milk and most dairy products back in 2001 and never went back. I still love cereal and my occasional Oreo dip, so I use nondairy milks. My favorites are cashew milk, hemp seeds milk, quinoa milk (complete protein), macadamia milk, soy milk (essential amino acids), hazelnut milk, and even coconut milk beverage. My least favorite is probably unsweetened almond milk as it doesn’t really have a good nutty flavor and very little protein, but that’s personal preference. Grocery stores and coffee shops offer many good options nowadays of vegan milk with different flavors, many of which are nut milks (non-dairy milk alternatives) or pea protein milk (4-5 grams of protein per cup) and even hemp milk, which is delicious.
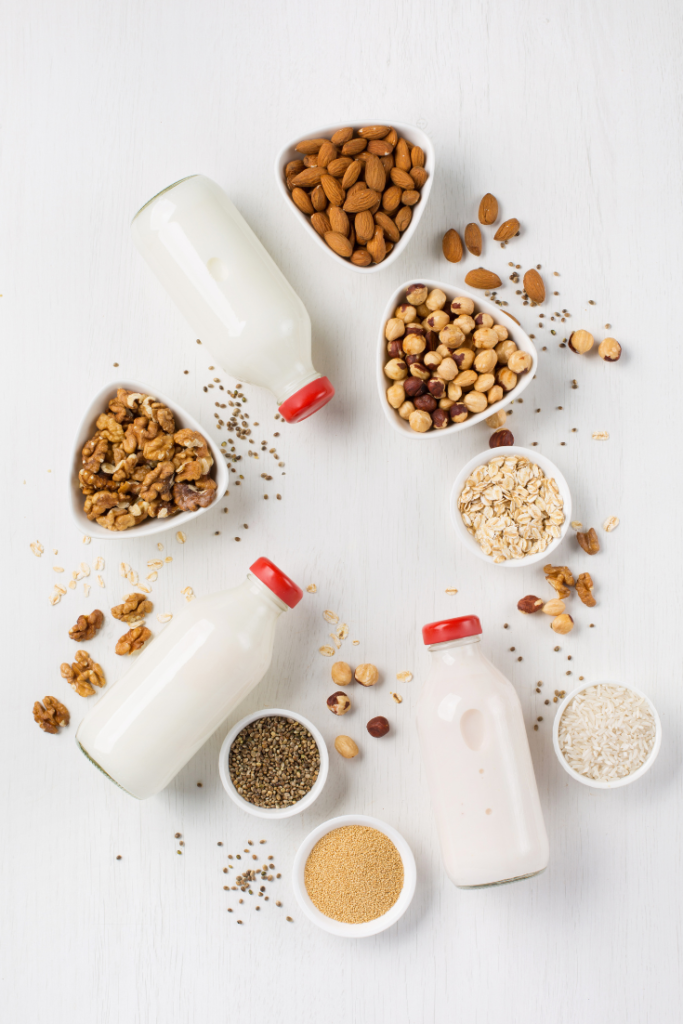



Non-dairy milks, also known as plant milk or alternative milks, have gained popularity in the past couple of years for several reasons. They mostly have a neutral flavor, many have short ingredient lists, and there are many unsweetened varieties with fewer calories, all of which are positive attributes. Plus, many people find them to be a suitable and nutritious option for various purposes. Here are some reasons why some individuals choose plant-based milk
Digestive Issues

- Lactose-Free Options: Many plant-based milks, such as almond milk, soy milk, and oat milk, are naturally lactose-free, making them suitable alternatives for individuals with lactose intolerance who experience digestive discomfort after consuming dairy.
- Easy Digestibility: Plant-based milks are often easier to digest compared to dairy milk, especially for those with sensitive digestive systems. They are lighter on the stomach and less likely to cause bloating, gas, or other digestive issues.
- Gentler on the Gut: Dairy milk contains proteins such as casein and whey, which can be difficult for some people to digest, leading to digestive discomfort. Plant-based milks are free from these proteins, making them gentler on the gut and reducing the risk of digestive upset.
- Reduced Inflammation: Dairy consumption has been associated with inflammation in the body, which can exacerbate digestive issues such as irritable bowel syndrome (IBS) or inflammatory bowel disease (IBD). Switching to plant-based milk can help reduce inflammation and alleviate digestive symptoms.
- Nutrient Variety: Plant-based milks offer a wide variety of options, each with its own unique nutritional profile. For example, almond milk is rich in vitamin E and calcium, while soy milk provides protein and essential fatty acids. Choosing different plant-based milks allows individuals to diversify their nutrient intake and support overall digestive health.
Dairy Allergies

- Elimination of Allergen: Plant-based milks are free from the proteins found in dairy milk, such as casein and whey, which are common allergens. By consuming plant-based milk instead of dairy milk, individuals with dairy allergies can avoid triggering allergic reactions.
- Hypoallergenic Options: Plant-based milks offer hypoallergenic alternatives for individuals with dairy allergies. Options like almond milk, soy milk, and rice milk are naturally free from dairy and are less likely to cause allergic reactions in sensitive individuals.
- Reduced Risk of Cross-Contamination: Plant-based milks are typically produced in facilities separate from dairy processing plants, reducing the risk of cross-contamination with dairy allergens. This can provide peace of mind for individuals with severe dairy allergies who need to avoid even trace amounts of dairy proteins.
- Diverse Nutritional Options: Plant-based milks come in a variety of options, each offering unique nutritional benefits. For example, soy milk is high in protein, almond milk is rich in vitamin E, and oat milk contains dietary fiber. By incorporating different plant-based milks into their diets, individuals with dairy allergies can still obtain essential nutrients without the risk of allergic reactions.
- Gentler on the Digestive System: Some individuals with dairy allergies may also experience digestive discomfort or inflammation when consuming dairy products. Plant-based milks are often easier to digest and gentler on the digestive system, providing relief from gastrointestinal symptoms associated with dairy consumption.
Inflammatory Response

- Lower Inflammatory Potential: Dairy products, particularly those high in saturated fats, have been associated with increased inflammation in the body. Plant-based milks, on the other hand, are generally lower in saturated fats and devoid of inflammatory compounds found in dairy, making them a better choice for individuals looking to reduce inflammation.
- Rich in Anti-inflammatory Nutrients: Many plant-based milks, such as almond milk, soy milk, and oat milk, contain beneficial nutrients with anti-inflammatory properties. For example, almonds are rich in vitamin E and antioxidants, soy contains isoflavones, and oats contain beta-glucans. These nutrients help combat inflammation and promote overall health and well-being.
- Avoidance of Potential Triggers: Some individuals may have sensitivities to components found in dairy milk, such as lactose or certain proteins, which can trigger an inflammatory response in the body. By switching to plant-based milk alternatives, individuals can avoid potential triggers and reduce the risk of inflammation-related symptoms.
- Supports Gut Health: Plant-based milks are often easier to digest compared to dairy milk, which can be beneficial for individuals with digestive issues or conditions such as irritable bowel syndrome (IBS) or inflammatory bowel disease (IBD). A healthy gut microbiome is essential for reducing inflammation throughout the body, and consuming plant-based milks can support gut health and reduce inflammation.
- Customized Nutritional Profile: Plant-based milks come in a variety of options, each offering a unique nutritional profile. Individuals can choose plant-based milks fortified with additional nutrients such as vitamins D and B12, omega-3 fatty acids, and calcium, which are important for reducing inflammation and supporting overall health.
Hormonal Imbalances

- Avoidance of Hormone Disruptors: Dairy products often contain hormones, such as estrogen and progesterone, which are naturally present in cows. These hormones can interfere with the body’s hormonal balance and exacerbate existing hormonal imbalances in individuals. Plant-based milks do not contain these animal-derived hormones, making them a preferable option for those looking to regulate their hormone levels.
- Reduction of Exogenous Hormone Intake: In addition to naturally occurring hormones, dairy cows may be treated with synthetic hormones to increase milk production. These exogenous hormones can potentially disrupt the endocrine system in humans and contribute to hormonal imbalances. By choosing plant-based milk alternatives, individuals can avoid exposure to these artificial hormones and support hormonal balance.
- Potential Reduction of Androgen Levels: Some studies suggest that dairy consumption may increase levels of certain hormones, such as insulin-like growth factor 1 (IGF-1) and androgens, which can affect hormonal balance and contribute to conditions like acne and polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS). Switching to plant-based milk may help reduce intake of these hormones and alleviate symptoms associated with hormonal imbalances.
- Supports Estrogen Metabolism: Certain plant-based foods, such as soy milk, contain phytoestrogens, which are plant compounds that have a weak estrogenic effect in the body. While the effects of phytoestrogens on hormonal balance are complex and context-dependent, some research suggests that they may help regulate estrogen levels and support overall hormonal health in certain individuals.
- Promotes Overall Health: Plant-based milks are often lower in saturated fats and cholesterol compared to dairy milk, which can have a positive impact on cardiovascular health and metabolic function. By improving overall health and reducing inflammation, plant-based milk alternatives can indirectly support hormonal balance in the body.
Bone Health
- Fortification with Calcium and Vitamin D: Many plant-based milks are fortified with calcium and vitamin D, essential nutrients for bone health. Calcium is crucial for building and maintaining strong bones, while vitamin D helps the body absorb calcium efficiently. Choosing fortified plant-based milks can help individuals meet their calcium and vitamin D needs, supporting overall bone health.
- Absorbable Calcium Sources: Plant-based milks derived from sources such as almonds, soy, and oats can provide calcium in forms that are easily absorbed by the body. While dairy milk is often touted for its calcium content, plant-based alternatives can offer bioavailable calcium without the potential negative effects of saturated fats and hormones found in dairy.
- Magnesium and Vitamin K: Some plant-based milks also contain magnesium and vitamin K, which play important roles in bone health. Magnesium helps convert vitamin D into its active form, promoting calcium absorption, while vitamin K contributes to bone mineralization and density. Including plant-based milks rich in these nutrients can complement calcium intake and support overall bone strength.
- Alkaline pH: Unlike dairy milk, which can have an acidic effect on the body, certain plant-based milks, such as almond and soy milk, have a more alkaline pH. Consuming foods and beverages with an alkaline pH may help balance the body’s pH levels and reduce calcium leaching from bones, potentially benefiting bone health in the long term.
- Low Saturated Fat Content: Plant-based milks are typically lower in saturated fats compared to dairy milk. High intake of saturated fats has been linked to increased bone loss and fracture risk. Choosing plant-based milks as part of a balanced diet can help reduce saturated fat intake while still providing essential nutrients for bone health.
Environmental Impact


- Lower Greenhouse Gas Emissions: Plant-based milk production generally requires fewer resources and generates fewer greenhouse gas emissions compared to dairy production. Producing plant-based milk typically involves fewer land use, water consumption, and carbon emissions, making it a more environmentally sustainable option.
- Reduced Water Usage: Dairy farming is water-intensive, requiring significant amounts of water for cattle hydration, cleaning, and crop irrigation. In contrast, plant-based milk production generally requires less water, as it involves growing crops such as almonds, soybeans, or oats, which have lower water requirements compared to dairy cattle.
- Lower Land Use: Dairy farming often involves extensive land use for grazing pastures and growing feed crops. By switching to plant-based milk, which relies on crops that can be grown more efficiently and on less land, individuals can help reduce deforestation and habitat destruction associated with expanding dairy operations.
- Mitigation of Pollution: Dairy farming contributes to environmental pollution through the release of methane emissions, nitrogen runoff, and manure disposal. Plant-based milk production tends to have a lower environmental impact in terms of air and water pollution, helping to mitigate environmental degradation and protect ecosystems.
- Sustainable Agriculture Practices: Many plant-based milk alternatives are produced using sustainable agricultural practices, such as organic farming, regenerative agriculture, and agroforestry. By supporting these practices, individuals can promote soil health, biodiversity, and ecosystem resilience, contributing to long-term environmental sustainability.
Ethical Concerns
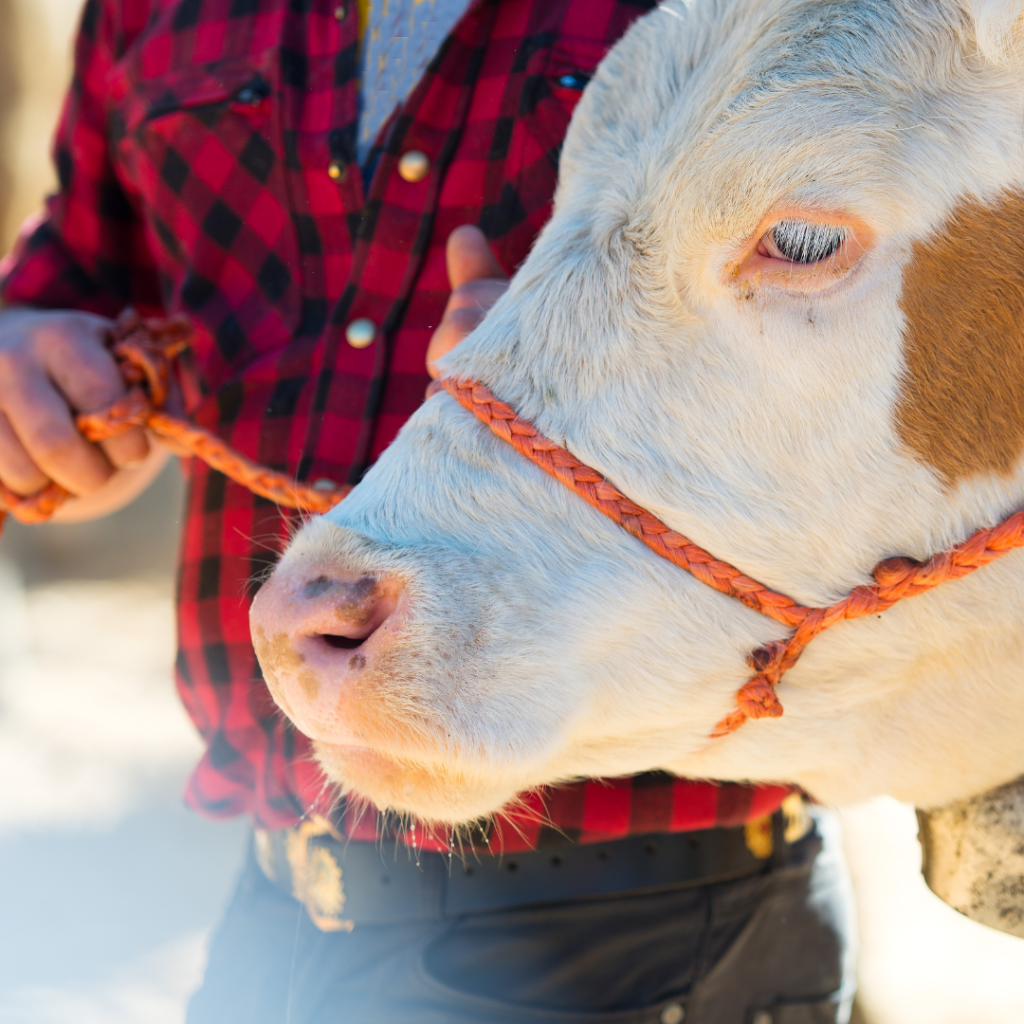

- Animal Welfare: Dairy farming often involves practices that raise concerns about animal welfare, such as confinement housing, separation of calves from their mothers, and routine use of antibiotics and hormones. By choosing plant-based milk alternatives, individuals can avoid supporting industries that may prioritize profit over animal welfare and contribute to the suffering of dairy cows and their calves.
- Cruelty-Free Choices: Plant-based milk production generally involves fewer ethical concerns compared to dairy farming. Plant-based milks are derived from crops such as almonds, soybeans, oats, and coconuts, which do not involve the direct exploitation or suffering of animals. Choosing plant-based milk allows individuals to make cruelty-free dietary choices aligned with their ethical values.
- Environmental Impact: Dairy production can have significant environmental consequences, including deforestation, habitat destruction, water pollution, and greenhouse gas emissions. By ditching dairy and opting for plant-based milk, individuals can reduce their environmental footprint and support more sustainable and ethical food systems that prioritize environmental stewardship and biodiversity conservation.
- Supporting Sustainable Agriculture: Many plant-based milk alternatives are produced using sustainable agricultural practices, such as organic farming, regenerative agriculture, and agroforestry. By supporting these practices, individuals can contribute to ethical food production systems that prioritize soil health, biodiversity, and ecosystem resilience while minimizing harm to animals and the environment.
- Promoting Compassion: Choosing plant-based milk over dairy milk reflects a commitment to compassion and respect for all living beings. By making ethical dietary choices, individuals can align their actions with their values of kindness, empathy, and non-violence, promoting a more compassionate and ethical world for humans and animals alike.
It’s important to note that the “best” choice depends on individual dietary needs, taste preferences, and health considerations. While plant-based milks offer benefits, they may not be nutritionally identical to dairy milk. Some plant-based milks may lack certain nutrients naturally present in dairy milk, such as calcium and vitamin B12, so it’s essential to choose fortified varieties or ensure a balanced diet that meets nutritional needs.
Favorite Home-Made Milk Alternatives



Get a Vitamix blender today and enjoy a creamy smoothie tomorrow!

