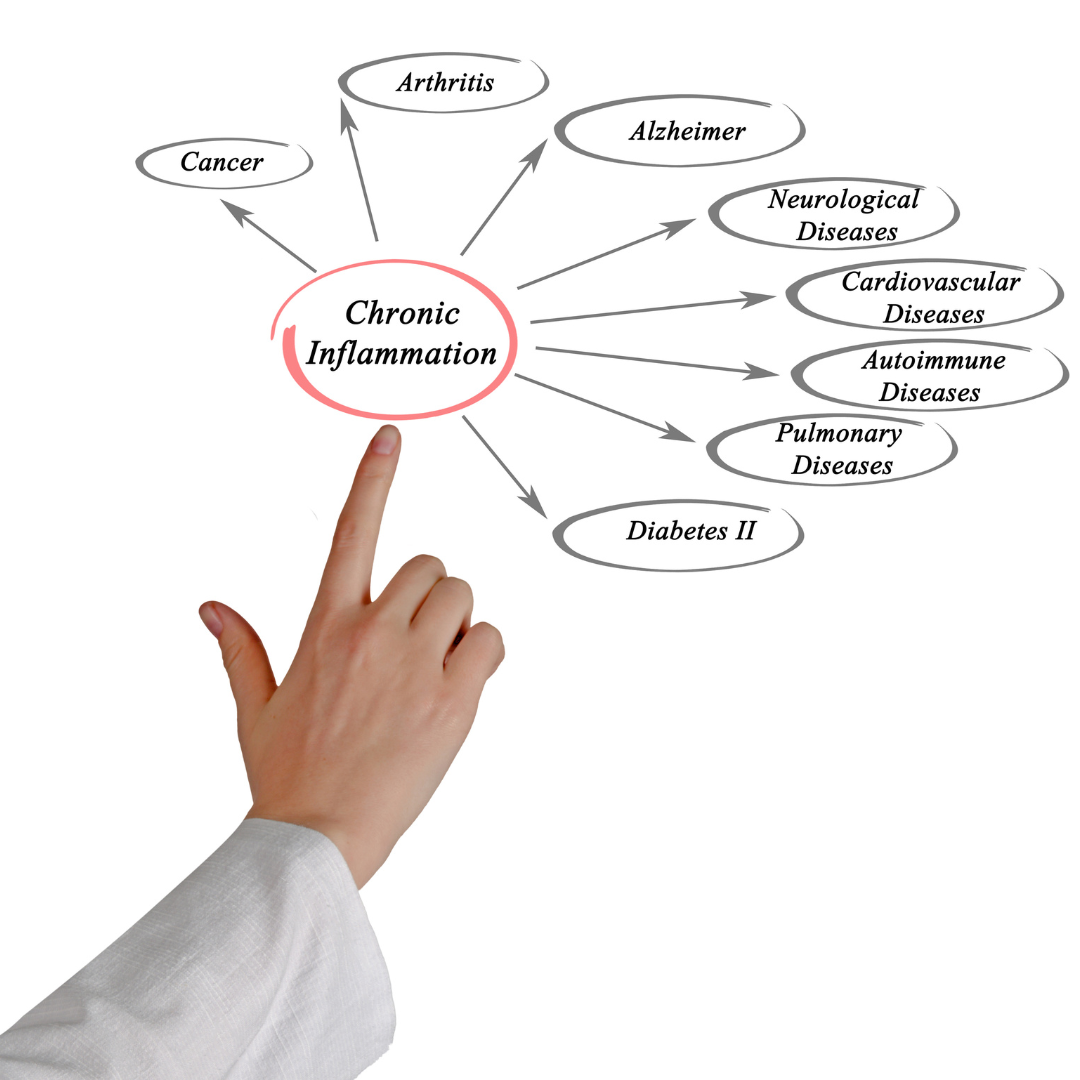
Inflammation in the Body & the Anti-Inflammatory Power of Food
We all know fruits and veggies are powerful but what else does the science tell us about inflammation?!
Chronic inflammation, a pervasive health concern, is increasingly recognized as a precursor to numerous chronic diseases, including heart disease, rheumatoid arthritis, and metabolic syndrome. In this in-depth exploration, we delve into the scientific foundations of chronic inflammation and the role of specific foods in crafting an anti-inflammatory diet.
Understanding Chronic Inflammation:
Chronic inflammation is characterized by a prolonged and dysregulated immune response, often triggered by environmental factors such as poor diet, sedentary lifestyle, and stress. Its association with various chronic diseases underscores the importance of adopting dietary strategies to combat this insidious health threat.
The Role of Fatty Acids:
Essential fatty acids, particularly omega-3 and omega-6 fatty acids, wield significant influence over inflammation. Fatty fish, such as salmon and mackerel, are rich in omega-3s, showcasing potent anti-inflammatory properties. Scientific research consistently supports the role of these fatty acids in modulating inflammation and mitigating the risk of chronic diseases.
Whole Grains – The Guardians Against Inflammation:
Whole grains emerge as stalwart allies in the fight against chronic inflammation. Scientific studies reveal that the fiber and phytonutrients in whole grains contribute to improved gut health and a reduction in inflammatory markers. Choosing whole grains over refined counterparts, like white bread, is a scientifically grounded strategy in fostering an anti-inflammatory diet.
Red Meat – A Double-Edged Sword:
While red meat is a valuable source of nutrients, excessive consumption has been linked to chronic diseases and heightened inflammation. Scientific evidence suggests that the compounds formed during the cooking process of red meat may contribute to inflammation. Balancing protein needs with plant-based sources and fatty fish can be a prudent approach to minimize inflammatory risks.
Mediterranean and Plant-Based Diets – A Scientific Triumph Against Inflammation:
Scientific research consistently extols the virtues of the Mediterranean diet in combating chronic inflammation. Rich in fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and healthy fats, this diet not only reduces inflammatory markers but also confers significant cardiovascular benefits. The Mediterranean diet stands as a scientifically validated blueprint for anti-inflammatory living.
Rheumatoid Arthritis – Unraveling the Link with Inflammation:
Scientific investigations have established a clear link between chronic inflammation and autoimmune conditions like rheumatoid arthritis. While genetics play a role, dietary choices can significantly impact the inflammatory response. The incorporation of anti-inflammatory foods, including fatty fish and olive oil, may provide relief for those battling rheumatoid arthritis.
Vitamin C – A Potent Anti-Inflammatory Weapon:
Scientifically recognized for its antioxidant properties, vitamin C plays a pivotal role in quenching free radicals and mitigating inflammation. Abundant in citrus fruits and berries, vitamin C has been associated with reduced inflammation and enhanced immune function, highlighting its crucial role in an anti-inflammatory diet.
The Influence of Monounsaturated Fats:
Monounsaturated fats, found in abundance in olive oil and avocados, showcase potent anti-inflammatory effects. Scientific studies elucidate how these healthy fats modulate inflammation at the cellular level, influencing gene expression and signaling pathways. The inclusion of monounsaturated fats stands as a scientifically backed strategy in crafting an anti-inflammatory diet.
Dark Chocolate – Scientifically Sweet Relief:
Scientific research provides a delectable revelation about dark chocolate – its flavonoids exhibit anti-inflammatory effects. Dark chocolate’s potential to reduce inflammation and improve cardiovascular health is supported by numerous studies. Moderation is key, but indulging in this scientifically proven sweet treat may confer health benefits beyond its delightful taste.
Cardiovascular Disease – A Terrain Shaped by Inflammation:
Scientific evidence unequivocally establishes the role of chronic inflammation in the development of cardiovascular disease. An anti-inflammatory diet, rich in omega-3 fatty acids, whole grains, and antioxidants, emerges as a preventive strategy, addressing inflammation at its root and promoting heart health.
Extra Virgin Olive Oil – Scientifically Documented Elixir:
Extra virgin olive oil, a cornerstone of the Mediterranean diet, is a scientifically documented elixir against inflammation. Its polyphenols exert anti-inflammatory effects, modulating cellular processes and reducing oxidative stress. Scientific studies consistently underscore the cardiovascular and anti-inflammatory benefits of this liquid gold.
Vitamin E – An Anti-Inflammatory Defender:
Scientific research highlights the anti-inflammatory prowess of vitamin E, abundant in nuts and seeds. This fat-soluble antioxidant scavenges free radicals, curtailing inflammation and bolstering immune function. Including vitamin E-rich foods in an anti-inflammatory diet is a scientifically supported strategy for overall health.
Free Radicals and Antioxidants:
At the core of chronic inflammation are free radicals – unstable molecules implicated in cellular damage. Antioxidants, abundant in fruits, vegetables, and nuts, counteract these free radicals, suppressing inflammation at the cellular level. Scientifically, the balance between free radicals and antioxidants is crucial for maintaining cellular health and thwarting chronic inflammation.
Weight Gain and Inflammation – Unraveling the Connection:
Scientific studies illuminate the intricate relationship between inflammation and weight gain. Adipose tissue, especially visceral fat, secretes inflammatory substances, contributing to a chronic inflammatory state. Adopting an anti-inflammatory diet, coupled with lifestyle modifications, is scientifically validated as an effective strategy for managing weight and inflammation.
Blood Flow and Inflammation:
Scientific investigations reveal the interconnectedness of blood flow and inflammation. Chronic inflammation adversely affects blood vessels, compromising their function and promoting cardiovascular diseases. An anti-inflammatory diet, with its focus on healthy fats and antioxidants, contributes to improved blood flow and vascular health.
Metabolic Syndrome:
Scientific literature underscores the association between chronic inflammation and metabolic syndrome – a cluster of conditions including abdominal obesity, high blood pressure, and insulin resistance. Adopting an anti-inflammatory diet has been shown to ameliorate these metabolic abnormalities, scientifically addressing the root causes of metabolic syndrome.
C-Reactive Protein – A Scientific Gauge of Inflammation:
C-reactive protein (CRP), a key biomarker of inflammation, has been extensively studied in the context of chronic diseases. Scientific evidence consistently links elevated CRP levels with an increased risk of heart disease and other chronic conditions. An anti-inflammatory diet, as supported by scientific research, contributes to lower CRP levels, indicating reduced inflammation and a lower risk of chronic diseases.
Conclusion:
In conclusion, the scientific landscape unequivocally supports the pivotal role of nutrition in modulating chronic inflammation. Incorporating foods rich in omega-3 fatty acids, antioxidants, and anti-inflammatory compounds is a scientifically sound strategy for promoting overall health and mitigating the risk of chronic diseases. From the scientifically validated benefits of the Mediterranean diet to the anti-inflammatory properties of dark chocolate, our dietary choices play a profound role in shaping the inflammatory landscape within our bodies. As we navigate this intricate connection between food and inflammation, armed with scientific insights, we empower ourselves to make informed choices that resonate with the principles of an anti-inflammatory lifestyle.