What Antioxidants In Foods Do For Your Health
Antioxidants are compounds that play a crucial role in protecting cells from damage caused by harmful molecules called free radicals. Free radicals are highly reactive molecules that can cause oxidative stress in the body, leading to various diseases and accelerating the aging process. Antioxidants neutralize free radicals by donating electrons, thereby preventing them from causing damage to cells.
Antioxidant-Rich Foods
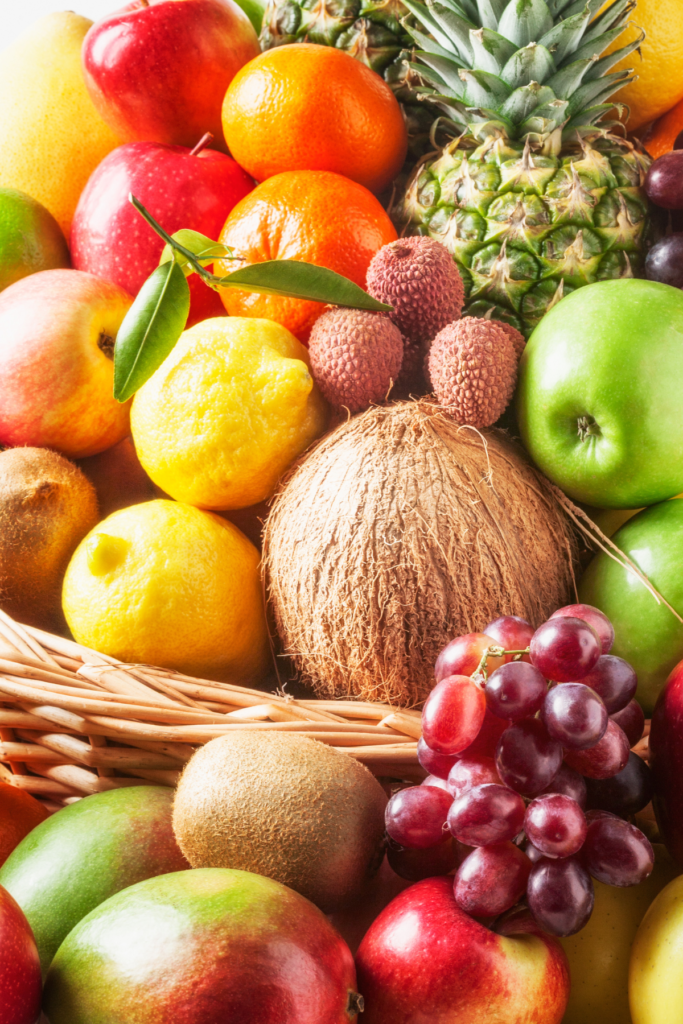
Colorful Fruits & Vegetables: Different colors in fruits and vegetables often indicate the presence of various antioxidants. Aim to include a rainbow of colors in your diet. Berries (blueberries, strawberries, raspberries), cherries, grapes, and citrus fruits are particularly rich in antioxidants.
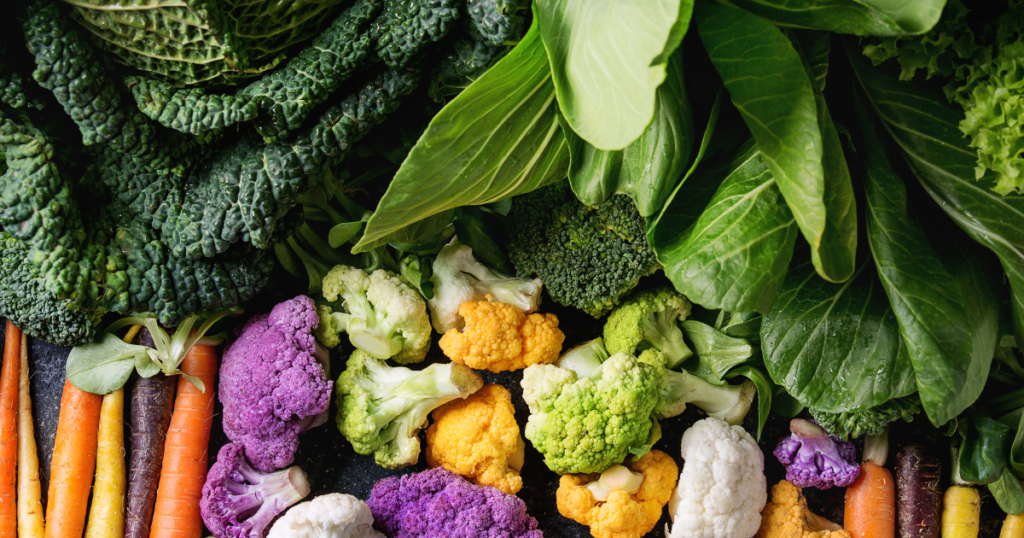


Dark Leafy Greens: Dark leafy greens such as spinach, kale, collard greens, and Swiss chard are packed with antioxidants like vitamins A, C, and K, as well as various phytochemicals
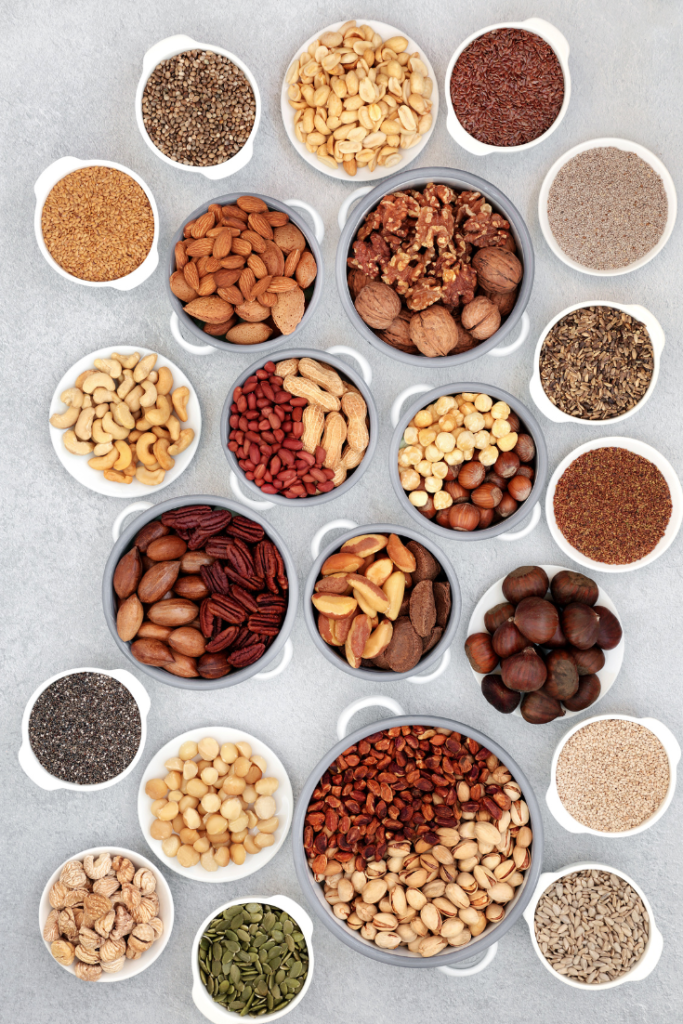
Nuts & Seeds: Almonds, walnuts, chia seeds, flaxseeds, and sunflower seeds are rich in antioxidants, healthy fats, and other essential nutrients.
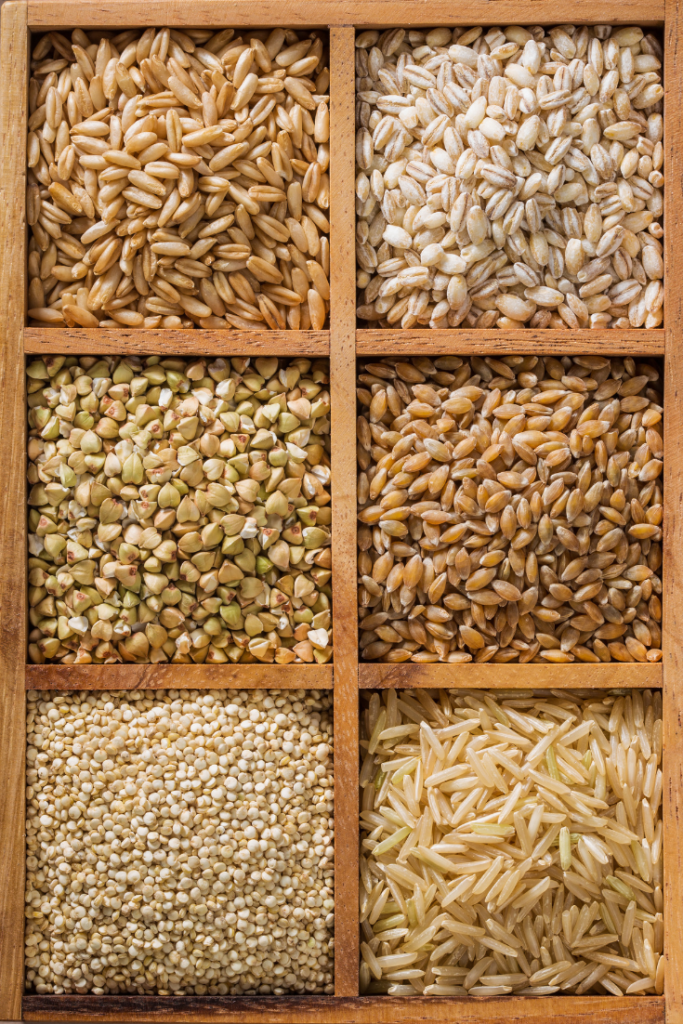


Whole Grains: Whole grains like quinoa, brown rice, and oats contain antioxidants and provide a good source of fiber.
Herbs & Spices: Many herbs and spices are rich in antioxidants. Examples include turmeric, cinnamon, ginger, oregano, and thyme
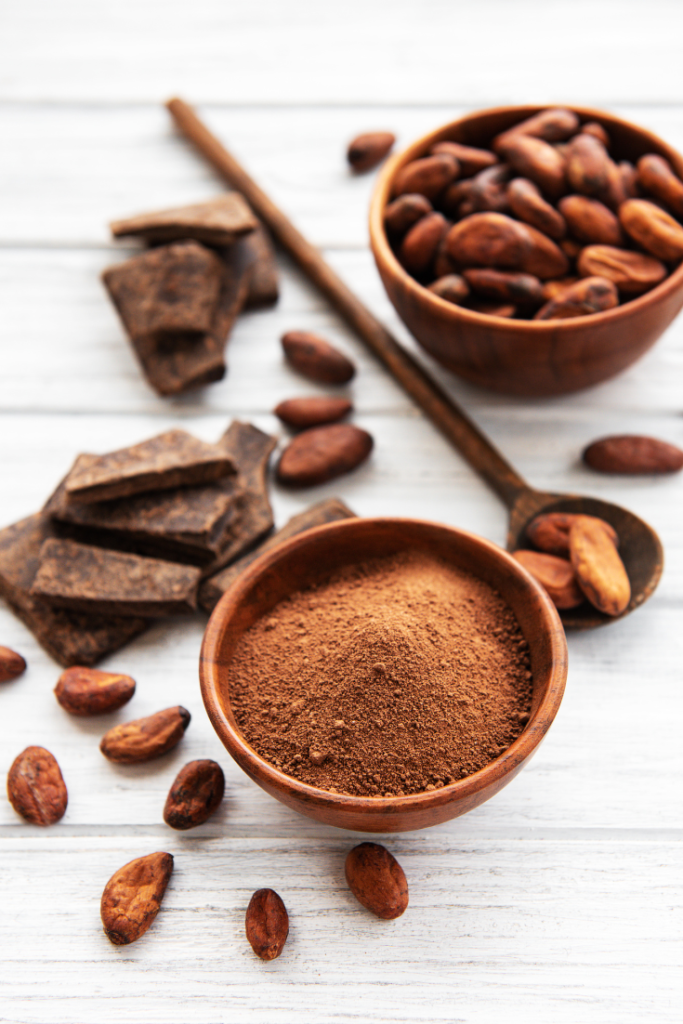

Dark Chocolate (in moderation): Dark chocolate contains flavonoids, which are antioxidants. Choose chocolate with a high cocoa content (at least 70%) for maximum benefits, and consume in moderation.
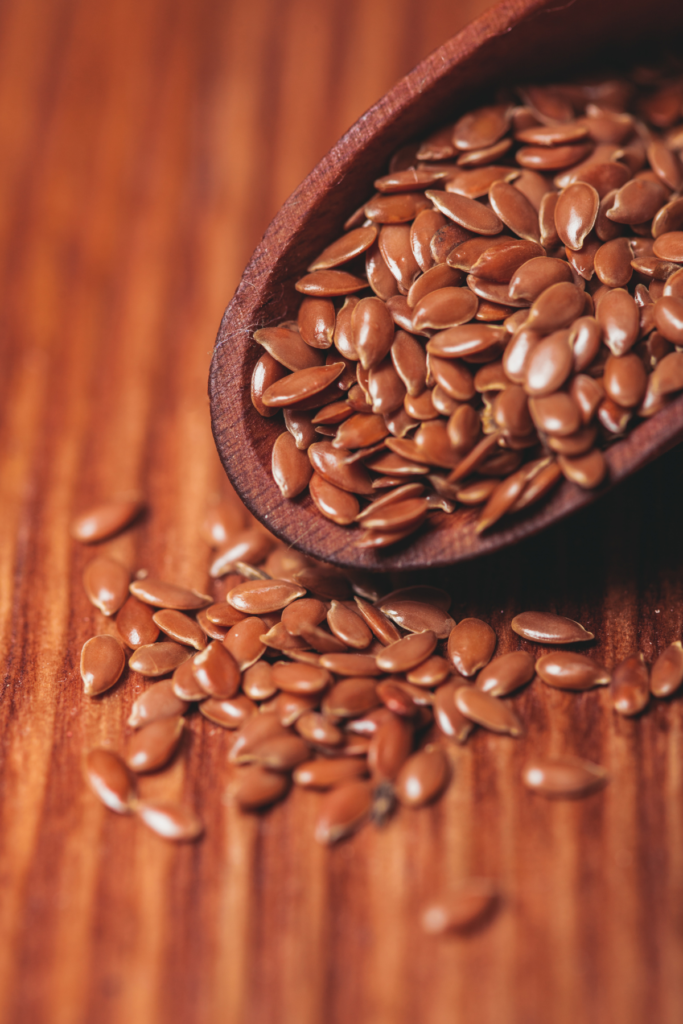


Omega-3 Fatty Acids: Foods rich in omega-3 fatty acids, such as flaxseeds, and walnuts, have anti-inflammatory properties and can contribute to overall health.
Antioxidant 101
- Types of Antioxidants:
- Antioxidants can be either endogenous (produced by the body) or exogenous (obtained from external sources, such as food or supplements).
- Common endogenous antioxidants include enzymes like superoxide dismutase, catalase, and glutathione peroxidase.
- Exogenous antioxidants include vitamins (such as vitamin C, vitamin E, and vitamin A), minerals (such as selenium and zinc), phytochemicals (such as flavonoids, carotenoids, and polyphenols), and other compounds like coenzyme Q10 (CoQ10).
- Sources of Antioxidants:
- Antioxidants are abundant in a variety of foods, particularly fruits, vegetables, nuts, seeds, whole grains, and legumes.
- Brightly colored fruits and vegetables, such as berries, oranges, tomatoes, spinach, kale, and bell peppers, are often rich in antioxidants.
- Other sources include green tea, dark chocolate, red wine, and certain spices like turmeric and cinnamon.
- Health Benefits of Antioxidants:
- Protecting against oxidative stress: Antioxidants help neutralize free radicals, reducing oxidative damage to cells and DNA.
- Supporting heart health: Some antioxidants, like flavonoids found in berries and cocoa, may help lower the risk of heart disease by improving blood flow and reducing inflammation.
- Enhancing immune function: Antioxidants support a healthy immune system by reducing inflammation and combating oxidative stress, which can help defend against infections and diseases.
- Anti-aging effects: By neutralizing free radicals, antioxidants may help slow down the aging process and reduce the appearance of age-related skin damage like wrinkles and fine lines.
- Lowering the risk of certain diseases: Consuming a diet rich in antioxidants has been associated with a reduced risk of chronic diseases, including cancer, neurodegenerative disorders (such as Alzheimer’s disease), and age-related macular degeneration.
- Supplementation and Considerations:
- While obtaining antioxidants from food is generally recommended, some people may choose to take antioxidant supplements.
- It’s important to note that excessive intake of certain antioxidant supplements may have adverse effects and even increase the risk of certain diseases. Therefore, it’s best to obtain antioxidants through a balanced diet rather than relying solely on supplements.
- Additionally, the effectiveness of antioxidant supplements in preventing disease or improving health outcomes is still a subject of debate, and more research is needed to fully understand their benefits and potential risks.
Let’s remember that a balanced and varied diet, along with a healthy lifestyle, is key to promoting overall health. Antioxidants are just one component of a well-rounded approach to nutrition and wellness. If you have specific health concerns or conditions, it’s advisable to consult with a healthcare professional or a registered dietitian for personalized advice.

