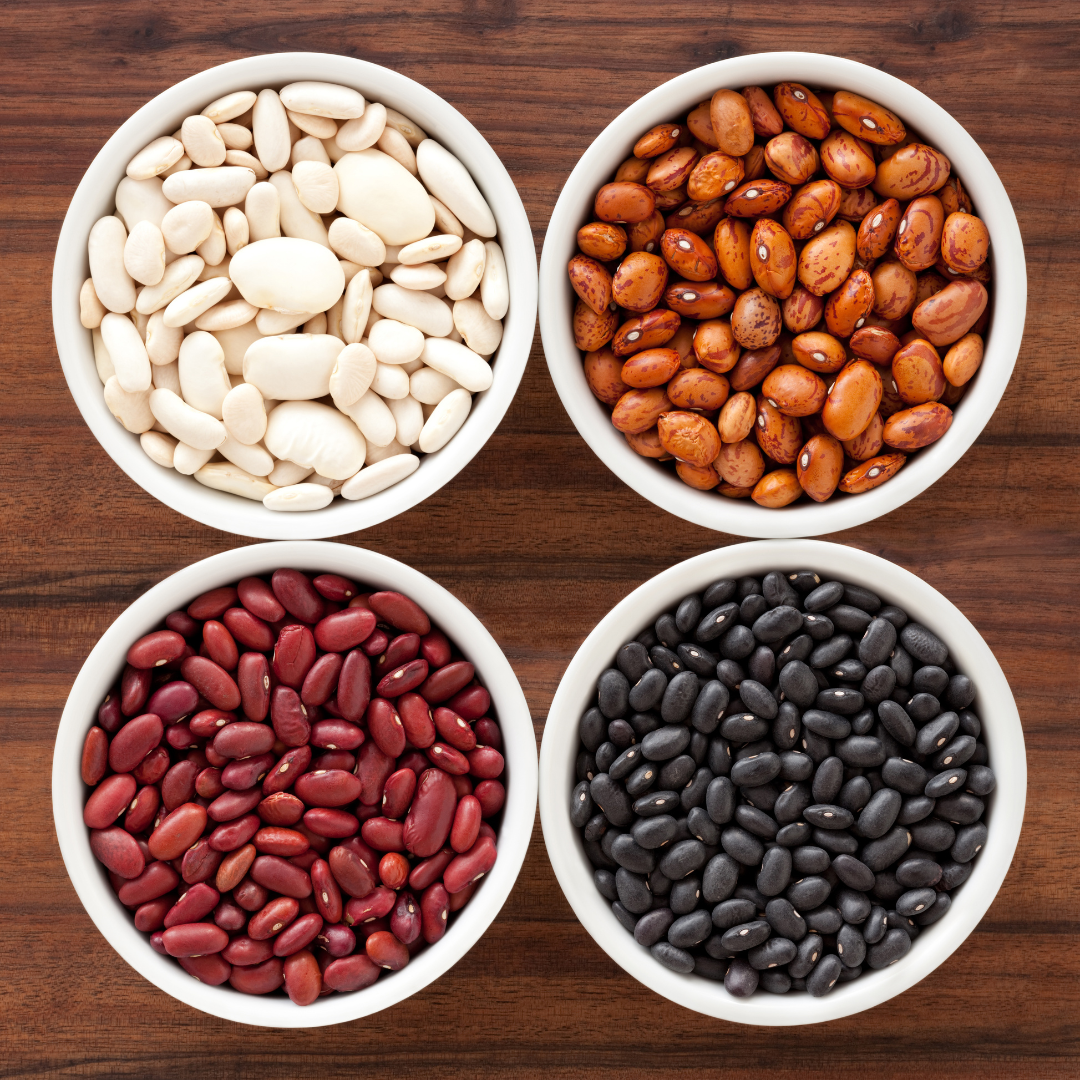
Beans: Unveiling the 12 Pillars of Health

If stranded on a desert island, my food of choice would be beans. Yes, beans! These humble legumes are nutrient-packed, versatile, and backed by science as a true powerhouse for both health and sustainability. Let’s explore why beans could be your best friend in any survival situation—or just your everyday diet.
1. Protein Power
Beans like black, kidney, and pinto are rich in plant-based protein, making them a top choice for muscle repair and overall body function. Protein is essential for health, and beans provide all the amino acids needed to meet daily requirements—without the environmental impact of animal protein.
2. Fiber for Digestion
Beans are fiber champions, promoting digestive health, helping to regulate blood sugar, and supporting weight management. Navy and green beans, in particular, are packed with dietary fiber, which helps you feel full, keeps your metabolism in check, and supports a balanced digestive system.

3. Heart Health
Beans are naturally low in saturated fat and packed with heart-friendly nutrients. Garbanzo beans, for example, are celebrated for their fat profile, which aligns with American Heart Association guidelines, making them a fantastic heart-healthy choice.

4. Micronutrient Goldmine
Beans are loaded with essential vitamins and minerals like folate, iron, potassium, and zinc. These nutrients play a role in many bodily functions, from red blood cell formation to immune health. Kidney and black beans are especially rich in these micronutrients, supporting everything from cellular health to bone strength.
5. Antioxidants for Defense
Beans are rich in antioxidants, which help combat inflammation and oxidative stress. Antioxidants in black and pinto beans, for instance, bolster your body’s defenses against cellular damage, which may reduce the risk of chronic diseases over time.

6. Reducing Chronic Disease Risk
Studies show that regular bean consumption is linked to a lower risk of chronic diseases like heart disease and diabetes. The unique blend of fiber, antioxidants, and plant-based protein in beans contributes to this reduced risk, making them a smart choice for long-term health.
7. Eco-Friendly Protein
Beans have a low carbon footprint compared to many animal products, making them a sustainable choice. Growing beans generates less greenhouse gas, aligning them with global sustainability goals and making them an environmentally conscious protein option.
8. Blood Pressure Benefits
Beans like kidney and black beans can help regulate blood pressure, thanks to their high potassium content and fiber. Including these beans in your diet could be a natural way to support cardiovascular health.

9. Weight Management and Blood Sugar Control
Beans are known for their high fiber content, which keeps you feeling full longer and can help with weight management. Additionally, beans have a low glycemic index, which means they help keep blood sugar stable—an advantage for anyone watching their glucose levels.
10. Affordable and Accessible
Beans are one of the most accessible and affordable superfoods out there. Available at any grocery store, whether canned or dried, they’re a budget-friendly way to improve your meals’ nutritional quality.

11. B Vitamins for Metabolism
Beans like garbanzo and green beans are also packed with B vitamins, essential for energy production and brain health. These nutrients support numerous processes in the body, making beans a great addition to a balanced diet.
12. Helping with Climate Change
Bean production is less resource-intensive than animal farming, making it a sustainable choice. By choosing beans over more environmentally demanding protein sources, you’re supporting global efforts to combat climate change.

The Bottom Line
Beans are more than a culinary staple—they’re a science-backed nutritional powerhouse! Whether for survival on a desert island or adding quality to your daily diet, beans are a superfood you can count on for protein, heart health, sustainable impact, and so much more. So go ahead, stock up, and let beans fuel you toward better health and a brighter future for the planet!
More Healthy Recipes